Swift + SQLite: Retrieve Data (SELECT)
In this tutorial, we'll explain how to retrieve data from a SQLite table using Swift.
We'll add the code for retrieving data in SQLite to the project from Swift - Update Data in SQLite (UPDATE).
Defining a Function to Select Data from the Students Table
Previously, we updated data in the students table, which stores values from the following Student struct:
struct Student {
var StudentID: Int
var StudentNumber: String
var FirstName: String
var LastName: String
var Age: Int?
init(studentID: Int, studentNumber: String, firstName: String, lastName: String, age: Int?) {
self.StudentID = studentID
self.StudentNumber = studentNumber
self.FirstName = firstName
self.LastName = lastName
self.Age = age
}
}
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS students (
student_id INTEGER NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
student_number TEXT NOT NULL,
first_name TEXT NULL,
last_name TEXT NULL,
age INTEGER NULL
);
This time, we'll create a getStudent function that retrieves data from the students table by specifying a StudentID.
Open DBService.swift and add the following code:
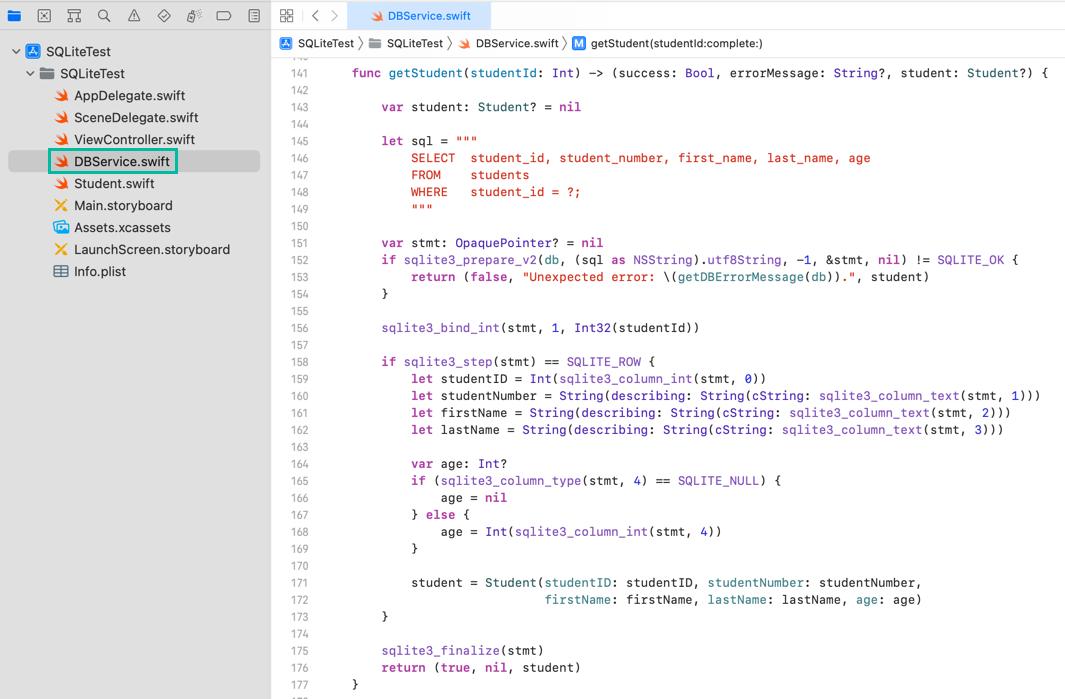
func getStudent(studentId: Int) -> (success: Bool, errorMessage: String?, student: Student?) {
var student: Student? = nil
let sql = """
SELECT student_id, student_number, first_name, last_name, age
FROM students
WHERE student_id = ?;
"""
var stmt: OpaquePointer? = nil
if sqlite3_prepare_v2(db, (sql as NSString).utf8String, -1, &stmt, nil) != SQLITE_OK {
return (false, "Unexpected error: \(getDBErrorMessage(db)).", student)
}
sqlite3_bind_int(stmt, 1, Int32(studentId))
if sqlite3_step(stmt) == SQLITE_ROW {
let studentID = Int(sqlite3_column_int(stmt, 0))
let studentNumber = String(describing: String(cString: sqlite3_column_text(stmt, 1)))
let firstName = String(describing: String(cString: sqlite3_column_text(stmt, 2)))
let lastName = String(describing: String(cString: sqlite3_column_text(stmt, 3)))
var age: Int?
if (sqlite3_column_type(stmt, 4) == SQLITE_NULL) {
age = nil
} else {
age = Int(sqlite3_column_int(stmt, 4))
}
student = Student(studentID: studentID, studentNumber: studentNumber,
firstName: firstName, lastName: lastName, age: age)
}
sqlite3_finalize(stmt)
return (true, nil, student)
}
Let's walk through the code for the getStudent function.
The input parameter is an Int type studentId. The return value is a tuple: (success: Bool, errorMessage: String?, student: Student?).
In lines 5–9, we define the SELECT statement and assign it to sql.
To execute SQL in SQLite, you must first prepare the statement and compile it into bytecode. Here, we use sqlite3_prepare_v2() to compile the SQL statement:
int sqlite3_prepare_v2(
sqlite3 *db, /* Database handle */
const char *zSql, /* SQL statement, UTF-8 encoded */
int nByte, /* Maximum length of zSql in bytes. */
sqlite3_stmt **ppStmt, /* OUT: Statement handle */
const char **pzTail /* OUT: Pointer to unused portion of zSql */
);
On line 11, we define stmt as an OpaquePointer? to hold the prepared statement handle. On line 12, we call sqlite3_prepare_v2() with the database handle, SQL statement, and &stmt. If it fails, we return false with the error message using getDBErrorMessage().
On line 16, we bind the studentId to the placeholder using sqlite3_bind_int().
On line 18, we execute the statement with sqlite3_step(). If the query returns data, it will return SQLITE_ROW.
If data is returned (lines 19–32):
- Line 19: sqlite3_column_int() retrieves the first column (student_id).
- Lines 20–22: sqlite3_column_text() retrieves the next three columns (student_number, first_name, last_name).
- Lines 24–29: Since age may be NULL, we check with sqlite3_column_type(). If it's NULL, assign nil; otherwise, use sqlite3_column_int() to get the value.
On lines 31–32, we create a Student object with the retrieved values. If no record with the given studentId exists, student remains nil.
On lines 35–36, we call sqlite3_finalize() to destroy the prepared statement and return the results.
Retrieving Data from the Students Table
Now let's use the getStudent() function to retrieve data. We'll retrieve the record with student_id = 1, which was updated in the previous article.
Update the code in ViewController.swift inside viewDidLoad() as follows:
//var student1 = Student(studentID: 1, studentNumber: "S000001", firstName: "Yuta", lastName: "Tanaka", age: 16)
//
//if DBService.shared.insertStudent(student: student1) {
// print("Insert success")
//} else {
// print("Insert Failed")
//}
//
//student1.LastName = "Yamada"
//student1.Age = 17
//
//if DBService.shared.updateStudent(student: student1) {
// print("Update success")
//} else {
// print("Update Failed")
//}
let (success, errorMessage, student) = DBService.shared.getStudent(studentId: 1)
if(success){
if let student = student {
print(student)
} else {
print("Student not found")
}
} else {
print(errorMessage ?? "Error")
}On line 18, we call DBService.shared.getStudent(studentId: 1) and store the return values in a tuple.
If success is true and student is not nil, we print the student.
If student is nil, we print “Student not found.”
If success is false, we print the error message.
Example output:
Opened connection to database
Student(StudentID: 1, StudentNumber: "S000001", FirstName: "Yuta", LastName: "Yamada", Age: Optional(17))
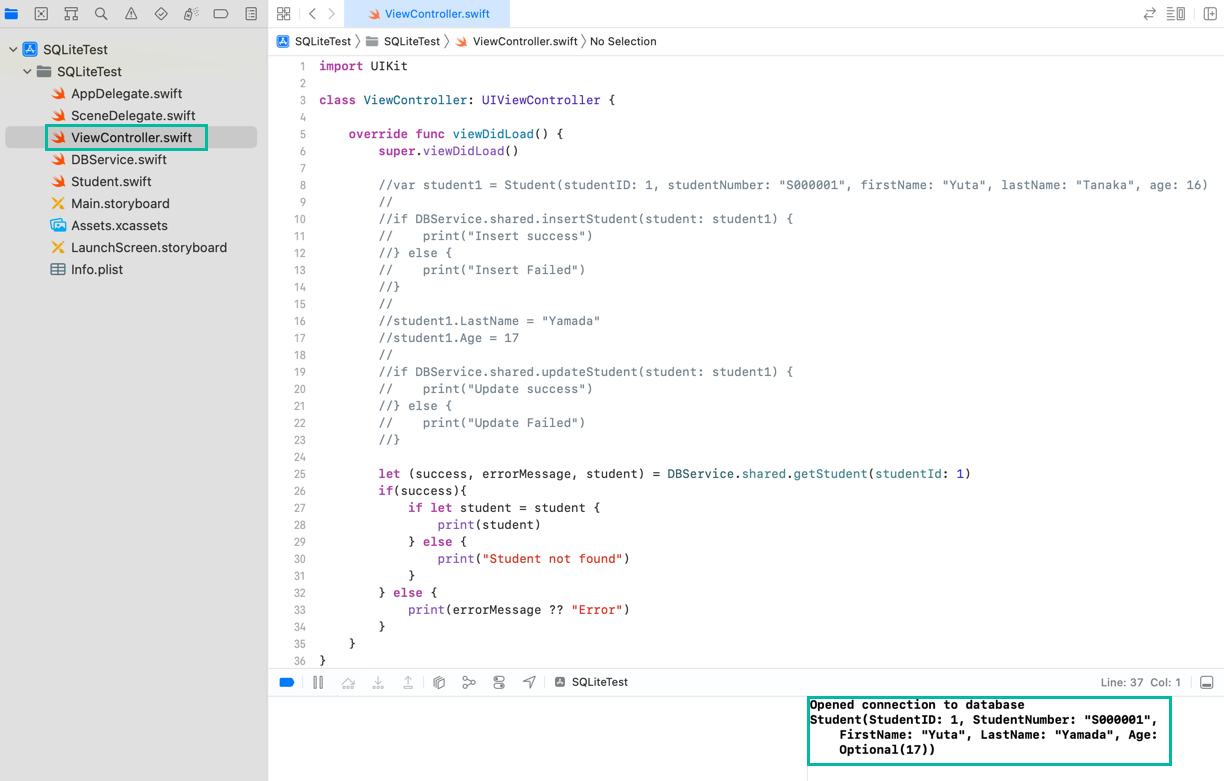
We successfully retrieved the student record with student_id = 1.
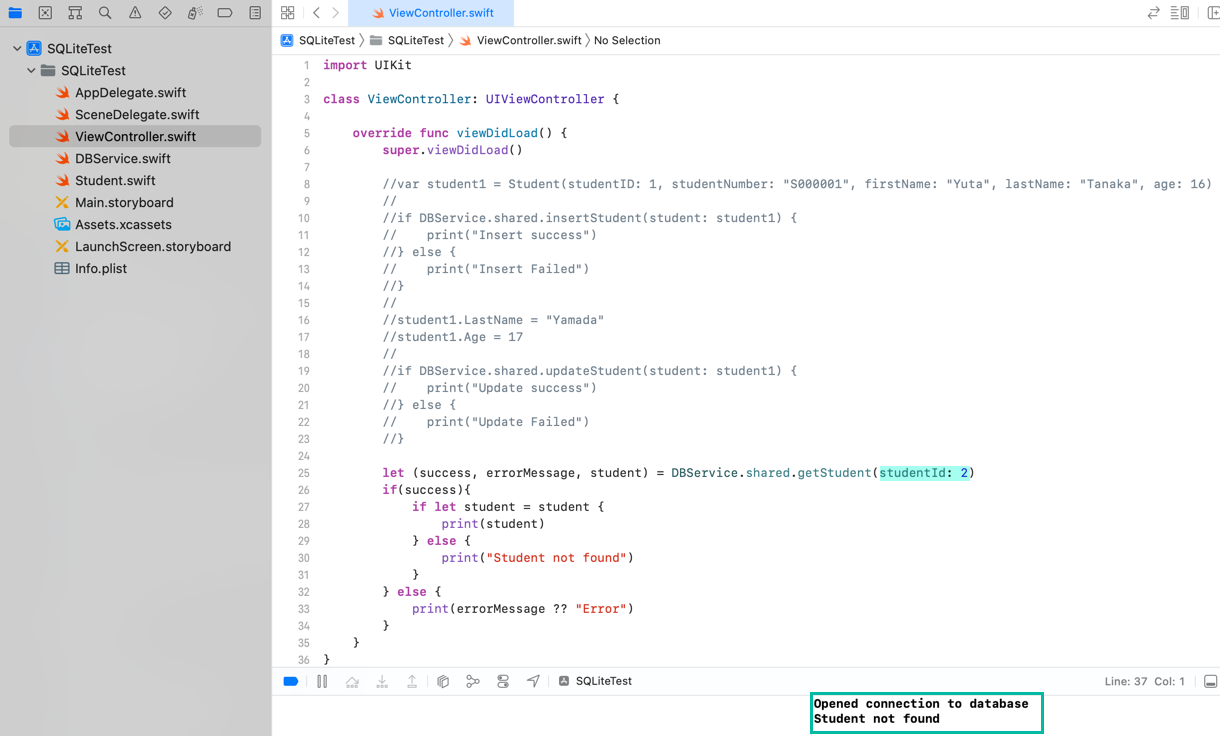
If we change the input studentId to 2, the output is:
Opened connection to database
Student not found
That's it — we've explained how to retrieve data from a SQLite table using Swift.
Next, we'll look at how to delete data from a SQLite table.