Swift Variables
In this article, we'll learn about Swift variables.
Variables and Constants in Swift
In programming, a "variable" is like a box with a name label that you can use to store data.
A "constant" is similar in that it also assigns a label to data, but once the initial value is set (initialized), it cannot be changed afterwards.
In Swift, you use the keyword var to define variables and let to define constants, like this:
- var variableName: DataType = value
- let constantName: DataType = value
We'll go over Swift data types in more detail on another page.
In the following code, the first line defines a variable named value1 of type String and assigns it the value "ABC." The second line defines a constant named value2 of type String and assigns it the value "XYZ."
var value1: String = "ABC"
let value2: String = "XYZ"The data type can be omitted. If omitted, the data type is inferred from the assigned value. Once set, the data type of a variable or constant cannot be changed.
- var variableName = value
- let constantName = value
var value1 = "ABC"
let value2 = "XYZ"You can also define variables and constants without assigning values right away.
- var variableName: DataType
- let constantName: DataType
var value1: String
let value2: String
value1 = "ABC"
value2 = "XYZ"value2 is a constant, but the assignment on line 5 is its initial assignment, so it does not cause an error.
If you want to change the value of a variable, you can assign it a new value. However, if you define it with let (making it a constant), trying to reassign a different value will cause an error.
var value1: String = "ABC"
let value2: String = "XYZ"
value1 = "ABC111"
value2 = "XYZ222"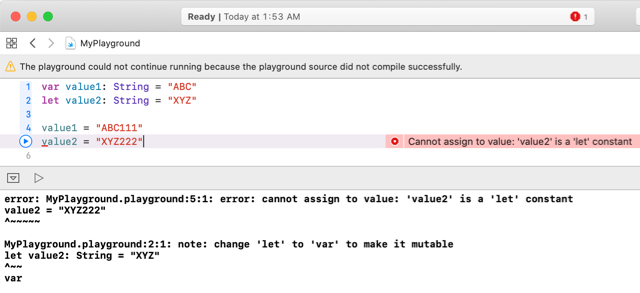
Naming Rules for Swift Variables
There are some rules when naming Swift variables. Constants follow the exact same rules.
- Names cannot begin with a number.
- Names cannot include whitespace characters, mathematical symbols like + or -, arrows, lines, or box-drawing characters.
- You cannot use reserved Swift keywords.
Even if you don't memorize these rules, Xcode will show an error message when you try to use an invalid name.
Other than that, you can actually use a wide variety of names. For example, the following variable names, such as Japanese characters or emojis, are valid, although I don't recommend using them.
var 変数名1 = "ABC"
var 🍇 = "Grapes"
print(🍇)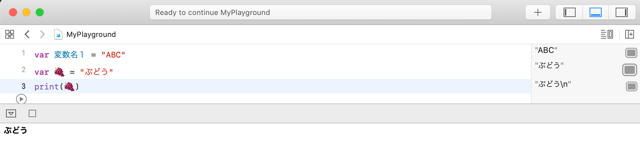
Also, Swift variable names are case-sensitive. This means that uppercase and lowercase versions of the same word are treated as different variables.
And that's it — now you know how to use variables in Swift.