Swift Operators
In programming, an "operator" is a symbol that represents a calculation or evaluation.
Operations include not only addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, but also comparing values and evaluating logical expressions.
In this article, we'll go over the basic Swift operators.
Arithmetic Operators in Swift
Arithmetic operators are intuitive since they are similar to those used in mathematics.
For example, if you want to add two variables a and b, you use the + operator and write a + b.
Common arithmetic operators in Swift include:
| Operator | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | a + b |
| - | Subtraction | a - b |
| * | Multiplication | a * b |
| / | Division | a / b |
| % | Remainder | a % b |
The % operator returns the remainder of a division.
For example, dividing 13 by 5 leaves a remainder of 3, so the following prints 3:
let a = 13
let b = 5
print(a % b)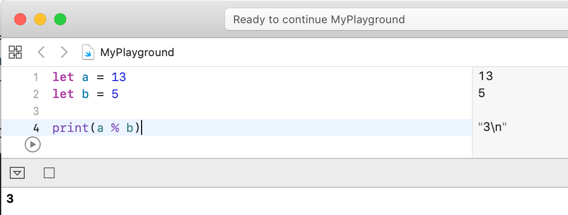
Comparison Operators in Swift
Comparison operators compare the values on the left and right, returning either true or false.
Common comparison operators in Swift include:
| Operator | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| == | a == b | a is equal to b |
| != | a != b | a is not equal to b |
| < | a < b | a is less than b |
| > | a > b | a is greater than b |
| <= | a <= b | a is less than or equal to b |
| >= | a >= b | a is greater than or equal to b |
| === | a === b | a and b reference the same instance |
| !== | a !== b | a and b do not reference the same instance |
let a = 5
let b = 6
print(a == b)
print(a < b)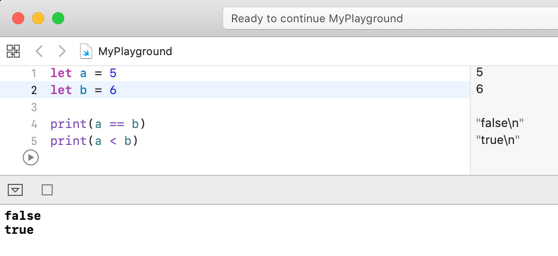
Assignment Operators in Swift
So far, you've seen assignments like value1 = "ABC". The = sign is one example of an assignment operator.
It means "assign the value on the right-hand side to the variable on the left-hand side."
Common assignment operators in Swift include:
| Operator | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| = | a = 2 | a = 2 |
| += | a += 2 | a = a + 2 |
| -= | a -= 2 | a = a - 2 |
| *= | a *= 2 | a = a * 2 |
| /= | a /= 2 | a = a / 2 |
| %= | a %= 2 | a = a % 2 |
var a = 1
a += 5 // 1 + 5 -> 6
a -= 4 // 6 - 4 -> 2
a *= 10 // 2 * 10 -> 20
a /= 4 // 20 / 4 -> 5
a %= 3 // 5 % 3 -> 2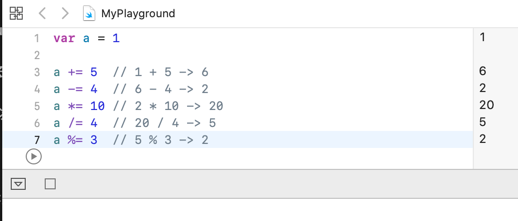
Logical Operators in Swift
Logical operators are useful when you want to combine and evaluate two true/false results.
Common logical operators in Swift include:
| Operator | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| && | a == b && a < 5 | Returns true only if both conditions are true |
| || | a == b || a < 5 | Returns true if either condition is true |
| ! | !(a == b) | Returns false if inside is true, true if inside is false |
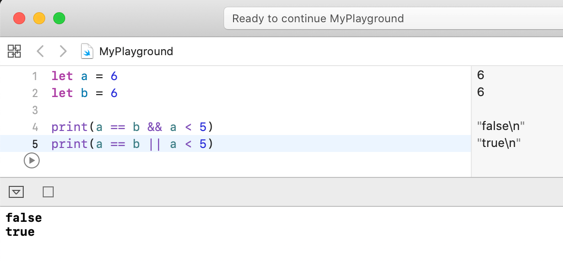
For example, if you want to check that "a equals b and a is less than 5," you can use the && operator as shown below:
let a = 6
let b = 6
print(a == b && a < 5)
print(a == b || a < 5)In line 4, since a == b is true but a < 5 is false, the whole expression evaluates to false.
In line 5, the || operator is used, and since a == b is true, the entire result is true regardless of the second condition.
Range Operators in Swift
Swift has range operators that make it easy to specify ranges.
| Operator | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| a...b | 1...10 | From 1 through 10 |
| a..<b | 1..<10 | From 1 through 9 |
| a... | 1... | From 1 to the end |
| ...b | ...10 | From the beginning through 10 |
| ..<b | ..<10 | From the beginning through 9 |
These range operators are often used in for loops and similar constructs.
That covers the most commonly used operators in Swift.